IN 2018 came into effect in Russiabiometric identification law. Banks are implementing biometric systems and collecting data for placement in the Unified Biometric System (Elementary school). Biometric identification gives citizens the opportunity to receive banking services remotely. This saves them from queues and technically allows them to “visit the bank” at any time of the day.
The convenience of remote identification by photo or voice was appreciated not only by bank clients, but also cybercriminals. Despite the desire of developers to make the technology safe, researchers are constantly reporting the emergence of new ways to deceive such systems.
So maybe, you should not agree to the friendly operator’s offer to undergo biometric identification at a bank branch? Or still take advantage of the new technology? Let's find out in this post.
What is the problem?
Biometric identification has its own peculiarities, which distinguish it from the usual login/password pair or “secure” 2FA:
- Biometric data is public. You can find photos, video- and audio recordings of almost any inhabitant of planet Earth and use them for identification.
- Can't replace a face, voice, fingerprints or retina with the same ease, as password, phone number or token for 2FA.
- Biometric identification confirms identity with probability, close, but not equal 100%. In other words, the system allows, that a person may differ to some extent from his biometric model, saved in the database.
Because biometrics don't just unlock airport turnstiles., but also bank safes, Hackers and cybercriminals around the world are hard at work on ways to deceive biometric identification systems.. Every year, the BlackHat information security conference program invariably includesreports, related to biometric vulnerabilities, but there are practically no performances, dedicated to the development of protection methods.
The main problems, related to biometric identification, falsification can be identified, leaks and thefts, low quality of collected data, as well as repeated collection of data from one person by different organizations.
Falsification
Publications, related to various methods of deceiving biometric identification systems, often found in the media. This andfingerprint of German Defense Minister Ursula von der Leyen, based on her public photographs, and cheating Face ID on iPhone X using a mask, sensationaltheft 243 one thousand dollars using the voice of the CEO faked by a neural network, fake videos with stars, advertising fraudulent winnings, and Chinese ZAO program, which allows you to replace the face of a video character with any other one.
To prevent biometric systems from mistaking photographs and masks for people, they use liveness detection technology - a set of various checks, which allow us to determine, that there is a living person in front of the camera, not his mask or photo. But this technology can also be deceived.
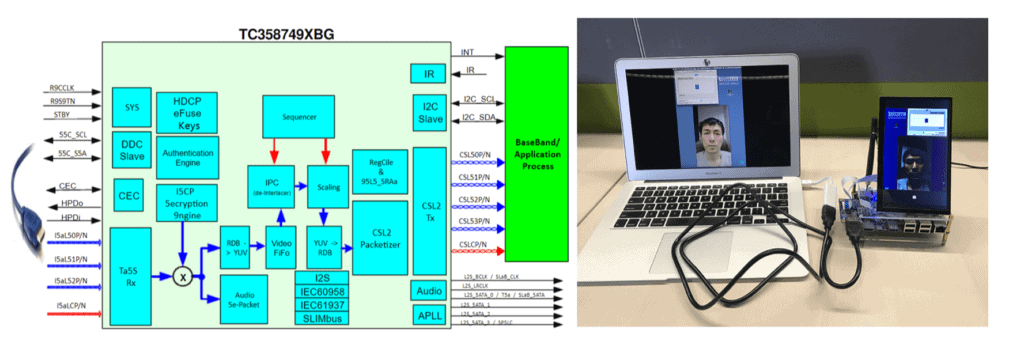
Injecting a fake video stream into a biometric system.Source
As presented at BlackHat 2019 report "Biometric Authentication Under Threat: Liveness Detection Hacking» reports of successful bypass of liveness detection in Face ID using glasses, placed on a sleeping person, introduction of fake audio- and video streams, and other ways.
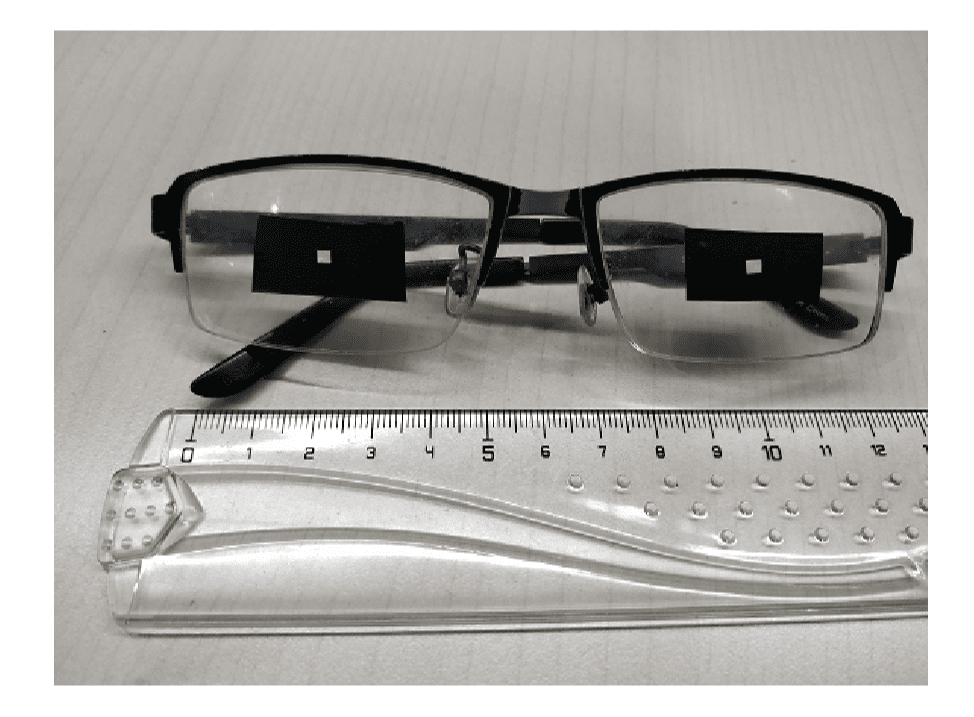

X-glasses - glasses for deceiving liveness detection in Face ID.Source
For user convenience, Face ID works, if a person is wearing sunglasses. At the same time, the amount of light in the eyes decreases, therefore, the system cannot build a high-quality 3D model of the area around the eyes. For this reason, finding glasses, Face ID does not attempt to extract 3D information about the eyes and represents them as an abstract model - a black area with a white dot in the center.
Quality of data collection and false recognitions
Identification accuracy is highly dependent on the quality of biometric data, saved in the system. To ensure sufficient quality for reliable recognition, equipment needed, which works in noisy and not very brightly lit bank branches.
Cheap Chinese microphones allow you to record a voice sample in adverse conditions, and budget cameras - take a photo to build a biometric model. But in such a scenario, the number of false recognitions increases significantly - the likelihood that, that the system will mistake one person for another, with a similar tone of voice or similar appearance. Thus, low-quality biometric data creates more opportunities to deceive the system, that attackers can take advantage of.
Multiple collection of biometrics
Some banks began implementing their own biometric system earlier, what EBS earned. Submitting your biometrics, man counts, that can take advantage of the new service technology in other banks, and when it turns out, it is not so, will submit the data again.
The situation with the presence of several parallel biometric systems creates a risk, What:
- In humans, who passed biometrics twice, more likely, the proposal to repeat this procedure will no longer be surprising, and in the future he may become a victim of scammers, who will collect biometrics for their criminal purposes.
- Leaks and abuse will occur more frequently, since the number of possible data access channels will increase.
leaks and thefts
It could seem, that the leak or theft of biometric data is a real disaster for their owners, But, in fact, it's not that bad.
In general, a biometric system does not store photographs or voice recordings., and sets of numbers, characterizing personality - biometric model. And now let's talk about this in more detail.
To build a face model, the system finds anthropometric reference points, defining its individual characteristics. The algorithm for calculating these points differs from system to system and is a secret of the developers. Minimum number of control points - 68, but in some systems their number is 200 and more.
Based on the found reference points, a descriptor is calculated - a unique set of facial characteristics, independent of hairstyle, age and makeup. Received handle (array of numbers) and is a biometric model, which is stored in the database. It is impossible to restore the original photo using the model..
To identify the user, the system builds his biometric model and compares it with a descriptor stored in the database.
There are important consequences from the principle of constructing the model:
- Use data, stolen from one biometric system to deceive another - it is unlikely to work due to different algorithms for searching for reference points and serious differences in the resulting model.
- It’s also not possible to deceive the system using data stolen from it - identification requires the presentation of a photograph or audio recording, on which a model will already be built and compared with the standard.
Even if the database stores not only biometric models, but also photos and audio, on which they are built, it is impossible to deceive the system with their help “head-on”: Liveness testing algorithms consider results with a complete match of descriptors to be false.
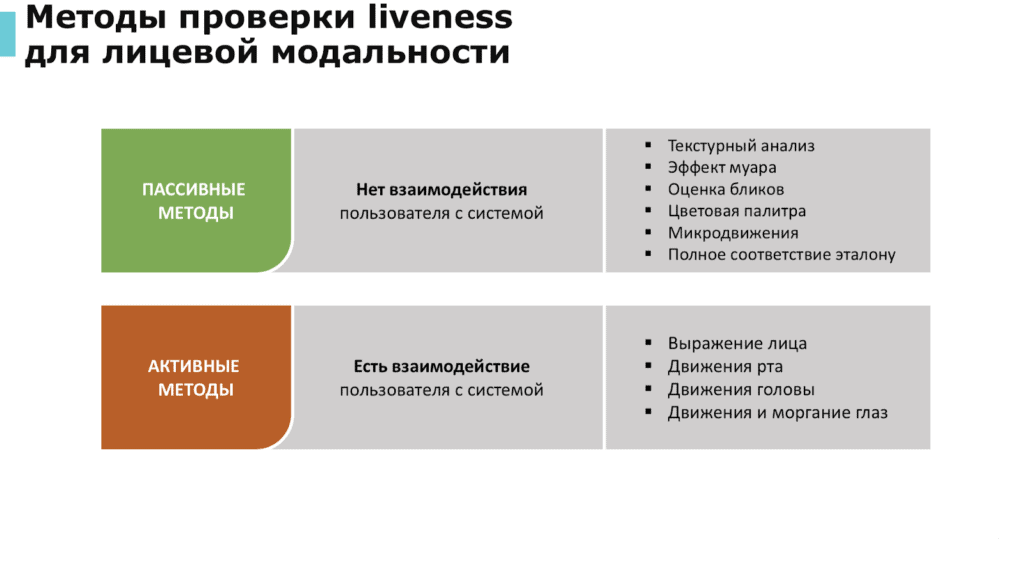
Liveness testing methods for facial and vocal modalities.
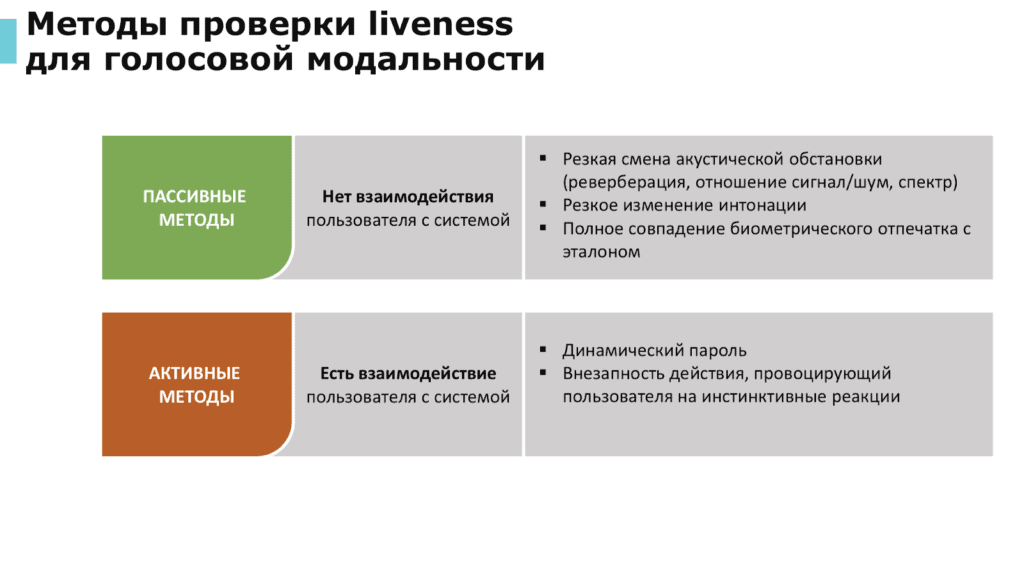
Source: Speech Technology Center
Thus, Using leaked biometric data will not help cybercriminals quickly gain material benefits, which means, they are more likely to look for easier and more reliable ways to get rich.
How to protect yourself?
Effective 14 September 2019 EU directive PSD2, also known as Open Banking, requires banks to implement multi-factor authentication to ensure the security of remote transactions, performed via any channel. This means the mandatory use of two of the three components:
- Knowledge - some information, known only to the user, For example, password or security question.
- Possessions - some kind of device, which only the user has, For example, phone or token.
- Uniqueness - something inalienable, inherent to the user and uniquely identifying the individual, For example, biometric data.
These three elements must be independent so, so that the compromise of one element does not affect the reliability of others.
In relation to banking practice, this means, that operations using biometric data must necessarily be accompanied by additional checks using a password, token or PUSH/SMS codes.
To use or not?
Biometric authentication has great promise, however the dangers, who come into our lives along with them, look very realistic. System developers and legislators should study the results of the latest research into the vulnerabilities of biometric systems and quickly refine both identification solutions, as well as regulations, regulating their work.
Banks need to take into account the situation with deepfakes and other ways to deceive biometric systems, using a combination of traditional methods of user identification with biometric: passwords, 2FA and USB tokens can still be useful.
The situation with bank clients is difficult. On the one side, biometric identification was developed for their convenience as an attempt to expand the ability to receive banking services at any time with minimal formalities. On the other hand, in the event of a successful attack, they are the ones who risk their money, and regulators and developers of biometric systems are not responsible for hacking.
Due to this, A logical recommendation to bank clients is not to rush to submit biometric data, ignore aggressive calls. If you can’t do without biometric identification, then use it in conjunction with multi-factor authentication, to at least partially reduce the risks.
Discover more from VirusNet
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.